Examples of Contingency Plan for Network Failure
When crafting a contingency plan for network failure, you should consider several key components. Start with clear documentation outlining response procedures for hardware malfunctions, software bugs, and human errors. Prioritize risks by evaluating their likelihood and impact. Include regular training sessions to prepare your team for these scenarios. You might reference real-world incidents, like the […]
Surviving the Storm: Mastering Disaster Recovery Plans in Hurricane Hotspots

It’s crucial to have solid disaster recovery plans in hurricane hotspots. This article will guide you through understanding the hurricane threat, assessing vulnerabilities, and developing a comprehensive recovery plan. You’ll also learn how to implement effective communication strategies and continuously improve your plan through testing. With this knowledge, you can confidently navigate the storm and […]
Preparing For The Unexpected: Key Examples Of Network Failure Contingency Plans

Network failures can significantly affect businesses and organizations in today’s interconnected world. The inability to access data, communicate with clients or customers, or conduct essential operations can result in financial losses and damage to reputation. Therefore, organizations must prepare for unexpected network failures by implementing robust contingency plans. One key aspect of network failure contingency […]
The Contingency Planning Guide
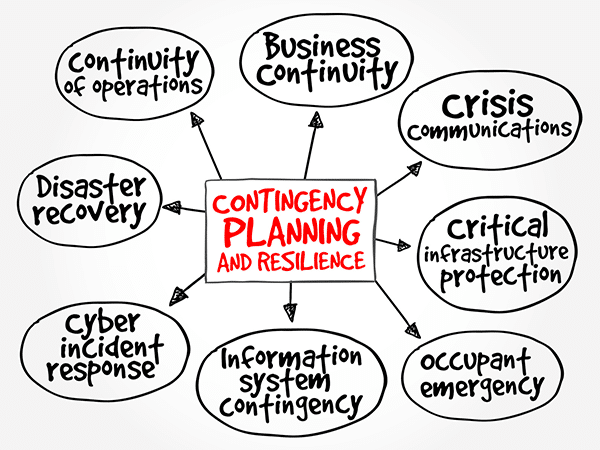
Sometimes a contingency plan (sometimes called a “Plan B”) is developed in case your chosen course of action doesn’t work out. A contingency planning guide is also a component of disaster recovery, business continuity scenarios and risk management that are part of nearly all business planning. Like this article mentions, a contingency plan is a course […]
Backup and Disaster Recovery: How Storing Data to a Cloud Can Benefit You

Backup and disaster recovery of your business’s data should be a top priority, no matter how small or large your business is. Anyone who doesn’t have some kind of backup system for their data in today’s time is playing as much risk as driving without car insurance. Regardless, deciding which method to use in backing […]