Aspects of Managed Services Support

Managed services and break-fix services play essential roles in supporting your business in IT-related matters. Small and medium entities face tough choices in deciding between the two aspects and complementing IT resources as well as personnel in place. Managed Services vs. The Break-Fix Mentality Just as the name suggests, the Break-fix mentality interacts with your […]
Computer Tip: Learn How To Keep Your Outlook Inbox Clean

An Outlook inbox that is constantly full is frustrating, and can make it more difficult to notice important emails. How do you maintain your Outlook inbox without spending hours each day? Microsoft Outlook has a couple of built-in features that help you quickly and continually keep your inbox clutter-free. Folders Perhaps the easiest and quickest way […]
Everything You Need To Know About Remote Data Backups

Remote data backups, also known as ROBO backup, is the practice of securely storing mission-critical data in remote offices. The advantage of this approach is that it allows an organization to keep all of its data in one place. Remote file backup services allow you to log into a remote drive and through an online […]
Business Computer Backup: How To Backup Your Computer To The Cloud
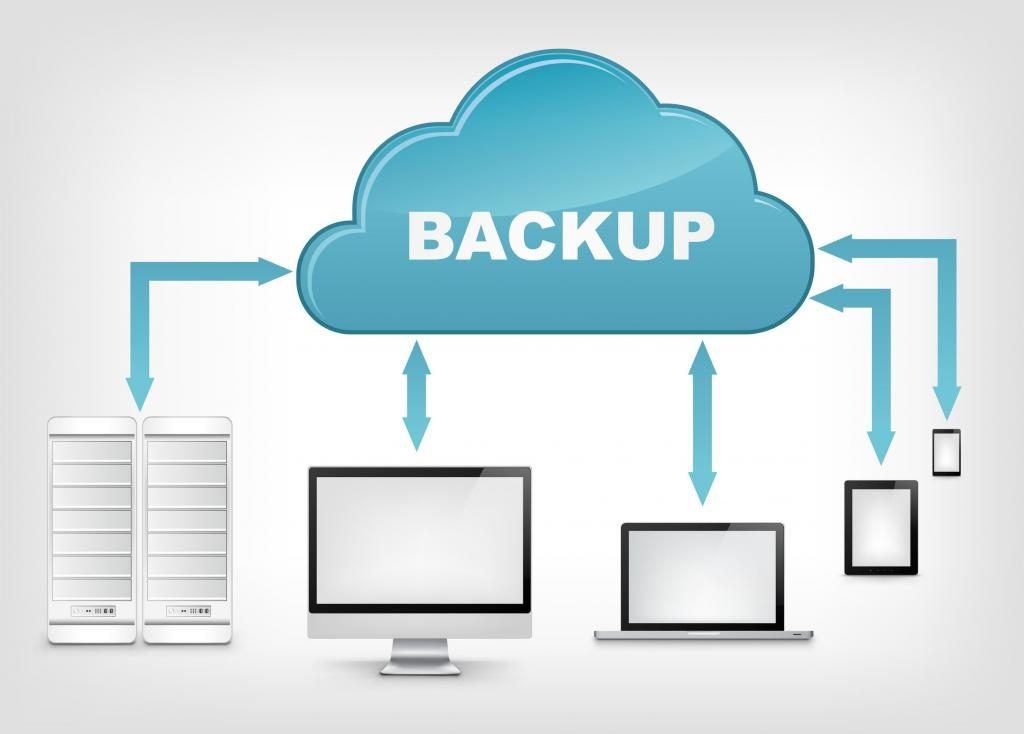
Cloud backups are the easiest form of backup to set up and maintain, and most services allow access to your files from various platforms. And learning about business computer backup is very important. To backup your files, create an account, download software, and input your account information. After this process, every time your computer goes […]
Don’t Become a Victim: Avoid Phishing Emails With These Tips

Phishing emails remain a popular method cyber criminals use to coerce users out of sensitive account information or to inject malicious code on a user’s machine. Individuals fall for phishing scams each day, leading to identity theft, security breaches, and exposure of confidential business data. According to the Anti-Phishing Work Group, 2016 was a record […]